Understanding Clean and Waste Water Pump Systems: Your Comprehensive Guide
May 22, 2025
Pump systems are critical components in ensuring effective water pressure management, wastewater handling, and flood prevention in residential, commercial, and industrial settings. From clean water booster pumps that maintain water pressure in multi-storey buildings to sewage pump stations that transport foul water to treatment facilities, each system plays a vital role in water and waste management. This guide explores how these systems work, key components, maintenance requirements, and the significant benefits they offer.
Above Ground Booster Pump Systems: Enhancing Water Pressure Efficiency

Booster pumps, also known as booster sets, are essential systems designed to maintain or increase water pressure in drainage networks, ensuring a reliable and consistent water supply. They are widely used in residential, commercial, and industrial buildings where existing water pressure is insufficient. Booster pump systems can typically be found above ground, in basements, or plant rooms. Here’s how they work:
- Water Supply Input: Water enters the booster set from a primary source, such as a mains water line, storage tank, or well. The incoming water pressure is usually lower than the desired level for end use.
- Pressurisation: Booster sets typically use one or more pumps, including centrifugal, submersible, or multistage pumps, to increase the pressure of the water. Pressure sensors monitor the system's water pressure and signal the booster pump to activate when pressure drops below a preset threshold.
- Distribution: Once pressurised, clean water is distributed through the plumbing system to taps, showers, and appliances. The booster set ensures consistent pressure even during peak demand or in multi-storey buildings where gravity can reduce pressure.
- Regulation and Control: Modern booster sets include electronic control units or variable speed drives (VSDs) that adjust pump speed based on demand, optimising energy use. Many systems also include a pressure tank to store pressurised water, reducing pump cycles and overall wear.
What Are the Key Components of a Booster Pump System?
- Pumps: Single or multiple pumps arranged in parallel to handle varying flow demands. Multi-pump systems activate additional pumps during high demand.
- Pressure Tank: Stores water and maintains consistent pressure, reducing pump cycles and extending pump lifespan.
- Control Panel: Manages pump operation and monitors system performance, featuring alarms for faults or low-pressure conditions.
- Valves: Check valves prevent backflow, and pressure relief valves ensure safety by releasing excess pressure.
What Are the Maintenance Requirements for Booster Pump Systems?
We recommend servicing your booster pump systems every 6 months to regularly inspect and clean the pumps, filters, valves, pressure tank, and sensors, ensuring they are functioning correctly and checking for signs of leaks, damage, or pressure loss.
What Are the Benefits of a Booster Pump System?
- Improved water pressure
- Energy efficient
- Reliable performance
- Flexible installation options
Below Ground Pump Stations: Managing Wastewater and Surface Water Effectively

What Are Sewage Pump Stations, and How Do They Work?
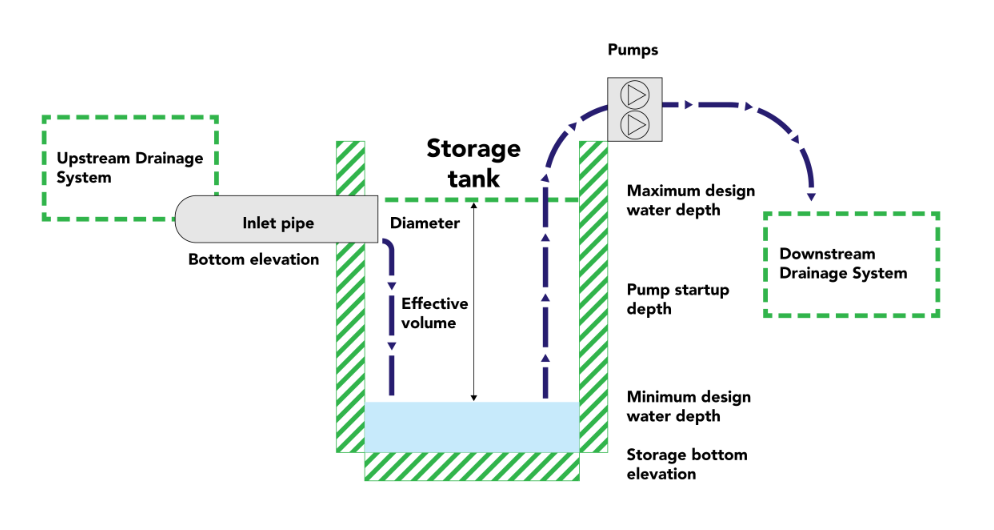
Sewage pumping stations are designed to handle sewage and wastewater from toilets, sinks, showers, and industrial discharge. These systems are typically installed underground where gravity flow is insufficient to transport wastewater to the main sewer line. Here’s how they work:
- Collection: Sewage water and wastewater flow into an underground wet well or collection chamber via pipes.
- Activation: Float switches or ultrasonic sensors monitor the liquid level in the wet well. When water reaches a set level, the submersible pump
- Pumping Operation: Pumps lift the wastewater from the wet well, directing it through a rising main to the main sewer or treatment plant.
- Discharge: Wastewater is discharged into a higher-level sewer system or treatment facility.
- Control and Monitoring: The control panel regulates pump operation and raises alarms for high water levels or pump malfunctions.
What Are Surface Water Pump Stations, and How Do They Work?
Surface water pump stations manage stormwater, rainwater, and surface runoff from roofs, roads, and car parks. These systems are typically installed in urban areas, car parks, or flood-prone zones to prevent flooding and water damage. Here’s how they work:
- Collection: Surface water flows into a wet well or collection chamber via gullies, drains, or channels.
- Activation: Sensors monitor water levels, and submersible pumps activate when levels reach a preset threshold.
- Pumping Operation: Pumps lift the surface water and direct it through a rising main to a watercourse, soakaway, or drainage system.
- Discharge: Clean water is safely discharged into natural waterways or storm drains.
- Control and Monitoring: Control panels manage pump operation and trigger alarms for faults or high-water levels.
What Are the Key Components of Below-Ground Pump Stations?
- Wet Well: Collection chamber for incoming water.
- Submersible Pumps: Pumps installed in wet wells to lift wastewater or surface water.
- Level Sensors: Monitor water levels and activate pumps.
- Control Panel: Automates pump operation and raises fault alarms.
- Rising Main: Pressurised pipe conveying water to the discharge point.
- Non-Return Valves: Prevent backflow into the wet well.
- Ventilation Systems: Safely vent gases in sewage water systems.
What Are the Key Differences Between Both Systems?
- Type of water handled: either sewage or surface
- Discharge point: sewer system or treatment plant if sewage, or watercourse, soakaway or storm drain if surface
- Design requirements: sewage stations must be equipped to handle solids and grease, whilst surface typically handles cleaner water
What Are the Maintenance Requirements for Below-Ground Pump Stations?
- Quarterly Service Visits: Essential for sewage pumping stations to inspect pumps, sensors, control systems, and wet wells.
- 6-Month Service Visits: Recommended for surface water stations.
- Annual Wet Well Cleans: Regular emptying and cleaning to prevent blockages and sewage odours.
What Are the Benefits of Below-Ground Pump Systems?
- Prevents flooding
- Reliable waste management
- Enables development
Get in Touch with the Pump Experts at Willow Pumps
For expert guidance on selecting, installing, or maintaining clean and waste water pump systems, contact us today. Our experienced team is ready to assist you in finding the best solution for your water and waste management needs.